Using Whois
What is a Whois Service?
ARIN offers public access to Internet resource registration data via a number of services. Traditionally, these services are known in the industry as “Whois” in reference to the public data service of ARPANET, the precursor of today’s modern Internet. Whois services are offered by all the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) like ARIN, most Internet Routing Registries (IRRs), and most domain name registries and registrars. The Whois protocol, originally specified in RFC 3912, is a query and response protocol that is used for querying databases that store registered users or assignees of an Internet resource, such as IP addresses, Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) or domain names. Whois is often referred to as “port 43” in reference to the TCP port number assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for the Whois protocol, and to differentiate it from other ways of getting Whois data.
ARIN’s Whois
ARIN’s Whois service is a public resource that allows a user to retrieve information about IP number resources, organizations, POCs, customers, and other entities.
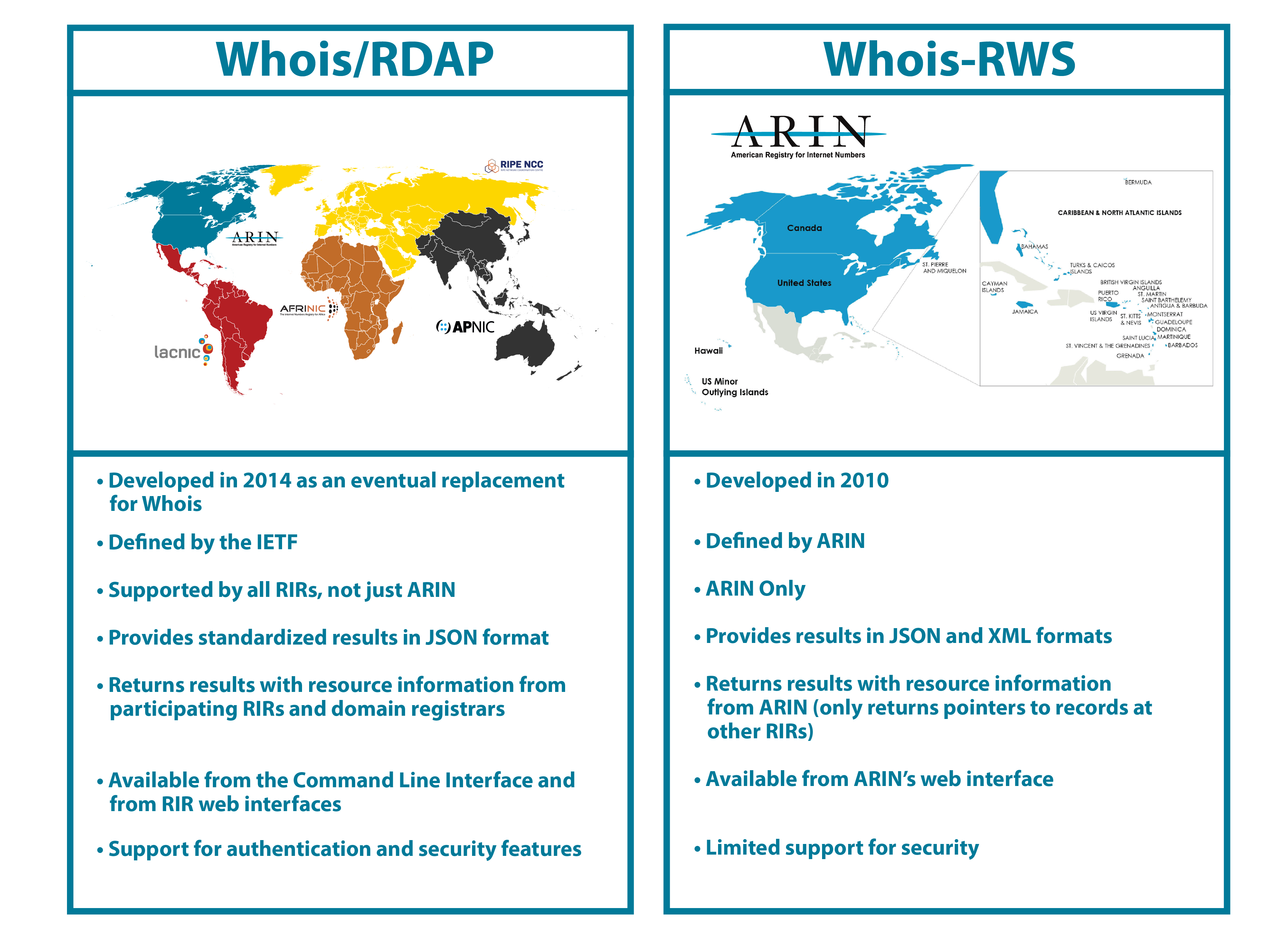
ARIN’s Whois/Registration Data Access Protocol (Whois/RDAP) service offers several ways for users to retrieve information from ARIN and other RIRs, IRRs, and registries that support RDAP. ARIN’s Whois-Restful Web Service (Whois-RWS) is an ARIN-specific service that allows users to query ARIN’s registration data by several methods.
Whois/RDAP
RDAP is a protocol that was developed, with IETF guidance, to offer a standardized way to query and retrieve registration data and to eventually replace traditional Whois. With the emergence of RDAP in 2015, ARIN began to implement support for RDAP and create its RDAP service. Unlike ARIN’s former primary Whois service, (Whois-RWS), RDAP allows users to search for and obtain information about not only ARIN-managed resources, but resources managed by other RIRs and domain name registries and registrars. RDAP responses are returned in JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), which is a machine-readable format that can be easily interpreted by a web interface, programming application, or software. At first, ARIN provided support for RDAP queries sent from the command-line interface or an RDAP client. In 2019, ARIN implemented a web interface to RDAP that allows users to enter search terms into a web search window and receive JSON information in easy-to-read HTML format, as shown in the following graphic.
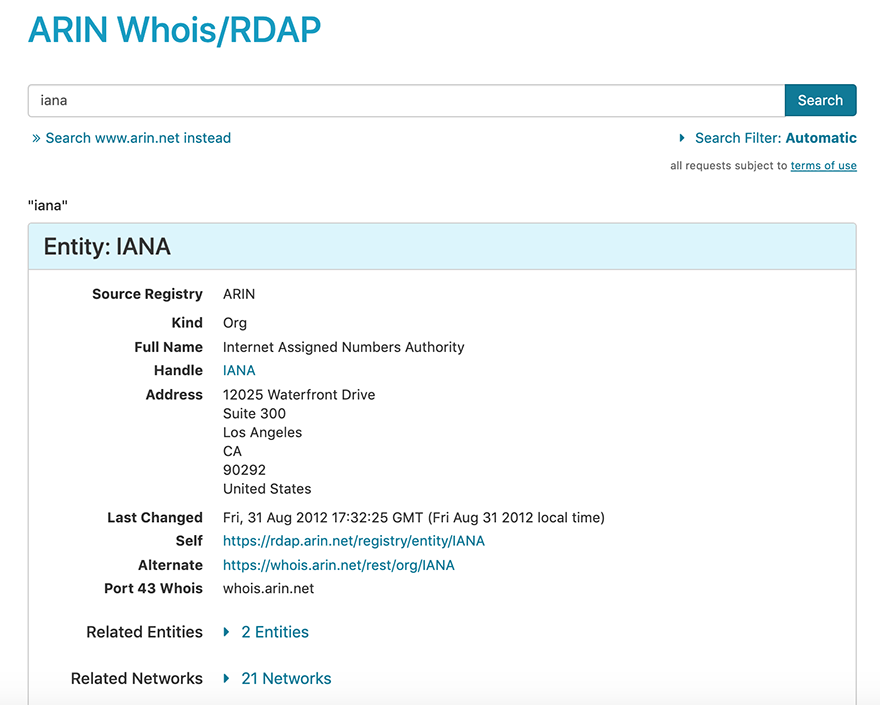
- Get instructions for using the Whois/RDAP web search in the using search sections of this page
- Access the Whois/RDAP web interface directly by visiting search.arin.net/rdap or using the “Search Site or Whois” field on arin.net pages
- Learn more about RDAP and its query and response structure by visiting Whois/RDAP
Whois-RWS
For many years, ARIN has provided information about the resources it manages using its own ARIN-specific Whois-RWS. This service allows users to obtain registration information from ARIN’s database for resources managed by ARIN, but provides limited information (such as reference records) for resources that are associated with other RIRs. The Whois-RWS web interface is shown in the following graphic.
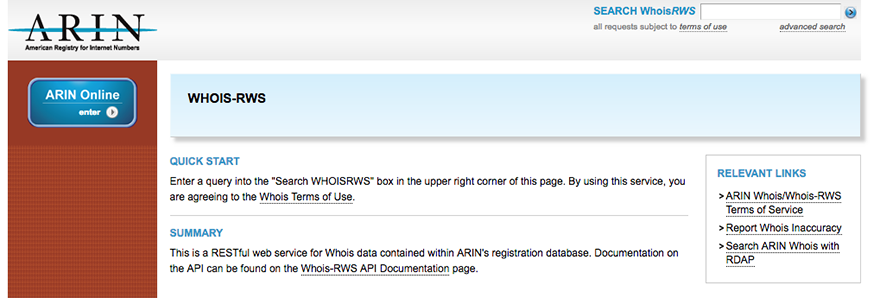
- Learn more by visiting Whois-RWS
- Access the Whois-RWS web interface by visiting whois.arin.net
As of 2019, ARIN has transitioned to Whois/RDAP as its featured Whois service, although Whois-RWS is still supported. RDAP provides these benefits that Whois-RWS does not:
- standardized query and response formats; that is, standardized input and output
- access to resource information from other generic top-level domain (gTLD) registries and registrars who implement RDAP
- support for authentication and security features
Using Whois from ARIN’s Web Site
To use ARIN’s web interfaces, refer to these instructions:
- To use the featured search, which can obtain information from ARIN and other registries and IRRs using RDAP, refer to the instructions in the following section.
- To use the older ARIN-specific Whois-RWS search, refer to Whois-RWS.
Using the Combined “Search Site or Whois” Feature on ARIN’s Web Site
ARIN provides access to Whois data (using Whois/RDAP) through its combined site search. Enter the information you want to search Whois for into the search box (labeled Search Site or Whois).

ARIN sends your query to search.arin.net, and returns results based on the type of search it guesses you were trying to perform. If you enter a search term that has a specific format, such as an IP address (for example, 2001:500:11::) or an ASN (for example, AS64496), the search engine automatically performs a Whois query and brings you the results.
If the search engine thinks you are searching for information about subject areas on the web site (for example, policy, services, or ARIN functions), it returns results from www.arin.net (you can then choose the Search ARIN’s Whois instead link on the results page to perform a Whois query), as shown in the following example.
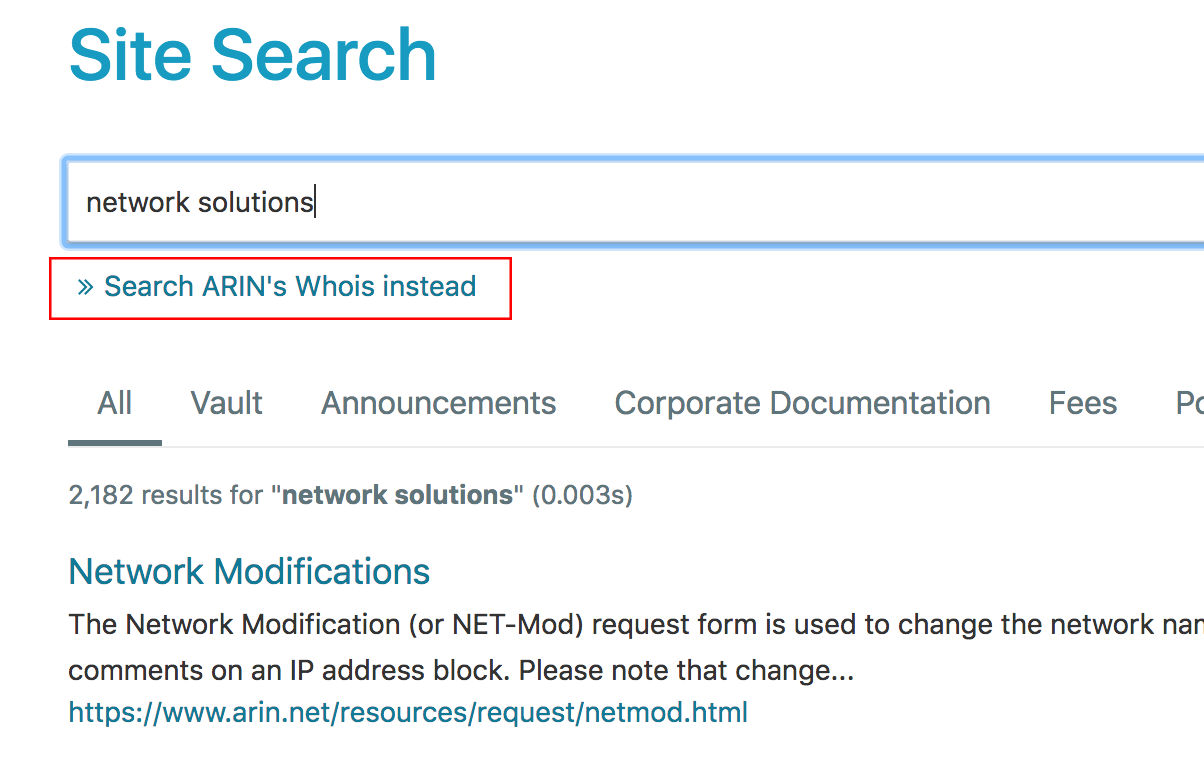
The following sections provide instructions on performing these common searches:
- Searching for an IP Address
- Searching for a CIDR Range
- Searching for an ASN/Autnum
- Searching for an Entity
- Searching for a Domain
- Searching for an Origin AS
Searching for an IP Address
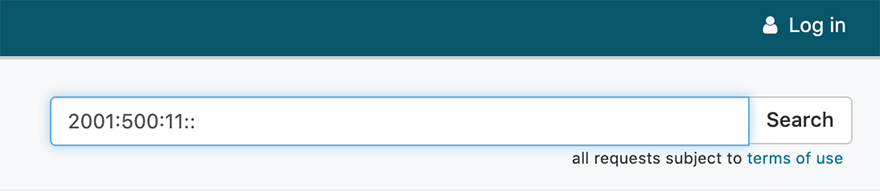
You can search for a network using its IPv4 or IPv6 address. Enter an IP address (for example, 2001:500:11::) in the Search Site or Whois field. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with an IP address search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
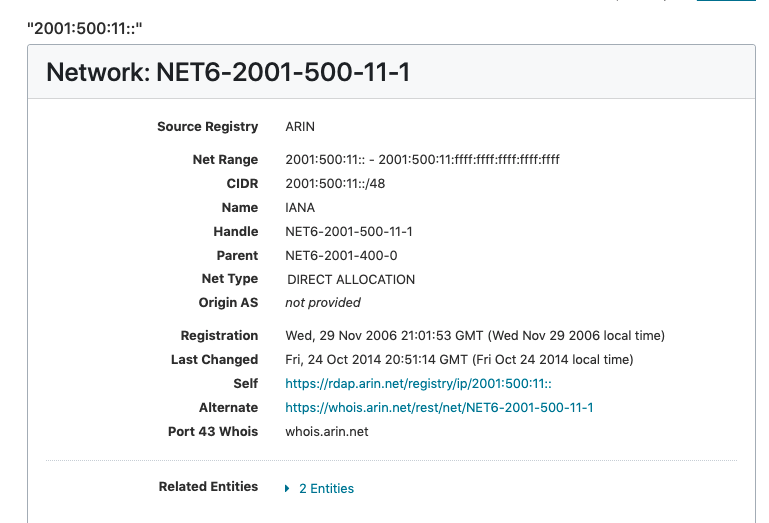
The search engine auto-detects that you are searching for an IP address and the network and related entities information for that IP address is returned.
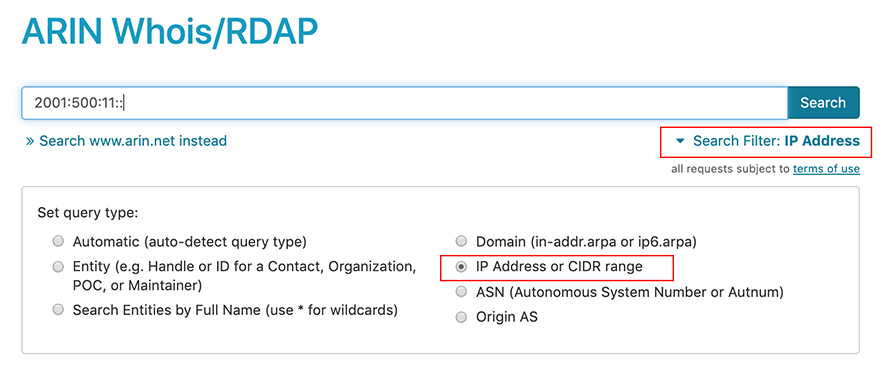
To narrow your search and query only in the IP address or CIDR range fields of Whois/RDAP, choose Search Filter and select IP Address or CIDR range. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with an IP address or CIDR search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
Searching for a CIDR Range
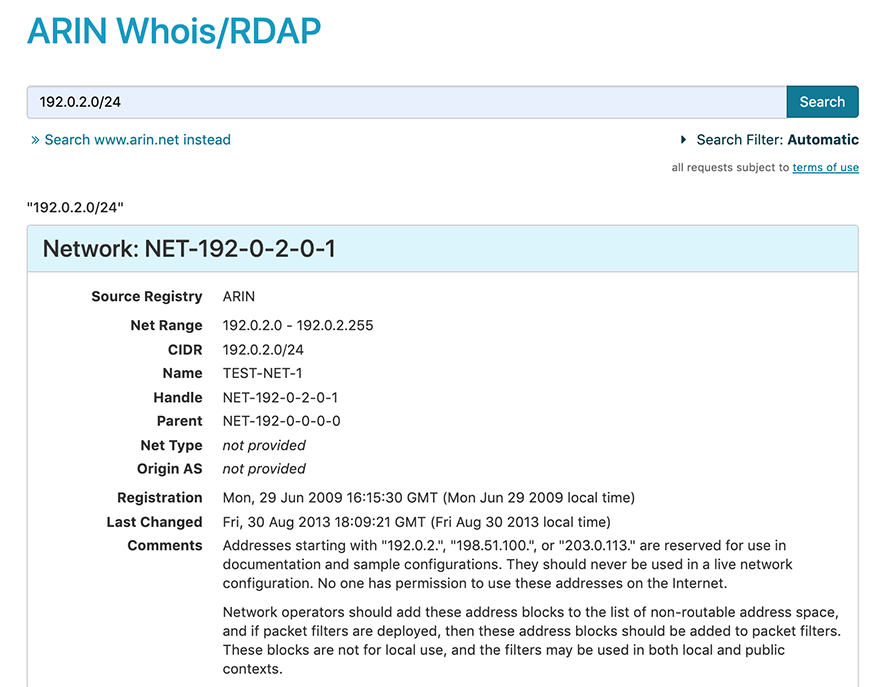
To search on a CIDR range (a block of IP addresses noted in CIDR format), enter the CIDR (in this example, 192.0.2.0/24) into the search field and choose Search. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with a CIDR search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
The search filter defaults to “automatic” and returns results based on the type of search that the search function guesses you were trying to perform. Due to the format of the search term, the search engine auto-detects that you are searching for a CIDR range and the network and related entities information for that CIDR range is returned.
 To narrow your search and query only in the IP address or CIDR range fields of Whois/RDAP, choose **Search Filter** and select **IP Address or CIDR range**. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks \*) with an IP address or CIDR search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
To narrow your search and query only in the IP address or CIDR range fields of Whois/RDAP, choose **Search Filter** and select **IP Address or CIDR range**. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks \*) with an IP address or CIDR search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.

Searching for an ASN
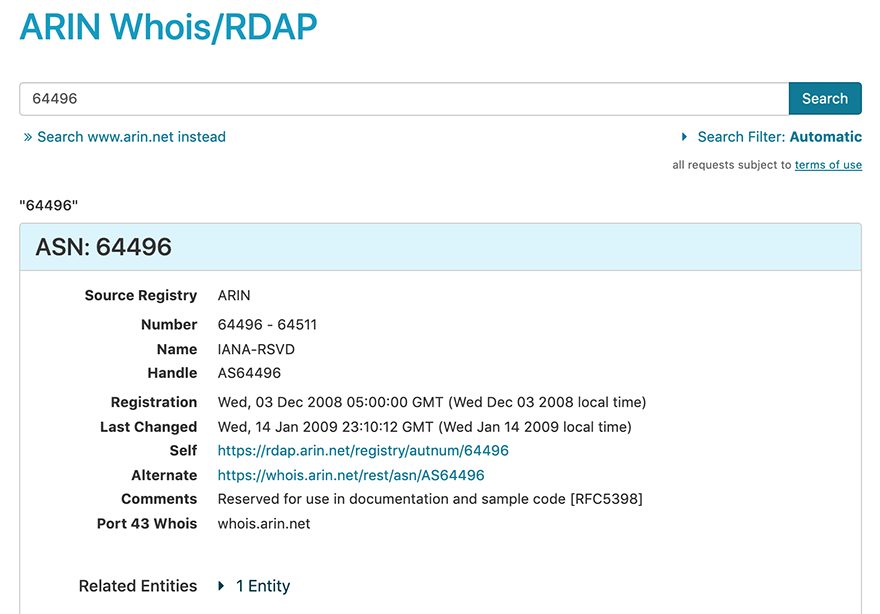
You can search for registration information pertaining to an ASN (also called an autnum in routing templates). In some registries, single ASNs are issued; in other registries, blocks of ASNs are issued. If the number in your query is part of a block, information for that single ASN in the range is returned. Different registries may have different formats for ASN data.
ARIN issues 4-byte ASNs, so to search for an ASN managed by ARIN, enter the number into the search field. (Entering the AS prefix is optional; for example, entering 64496 will automatically detect you are searching for an ASN matching this number and the information for the ASN is returned.) You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with an ASN search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
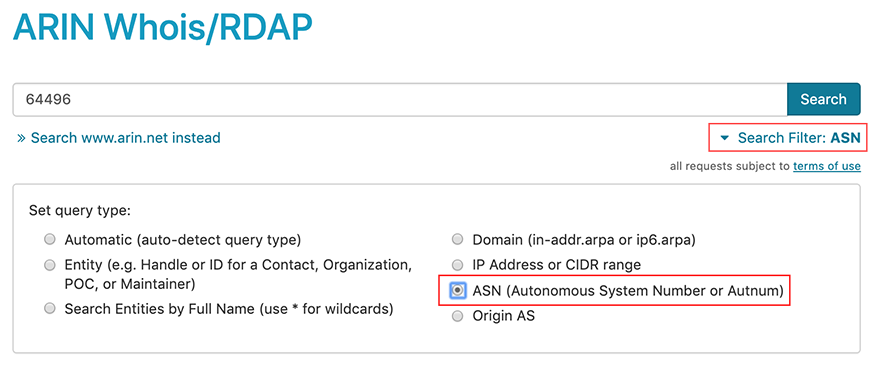
 To narrow your search and query only in the ASN field or the `autnum` field (in the routing templates) of Whois/RDAP, choose **Search Filter** and select **ASN (Autonomous System Number or Autnum)**.
To narrow your search and query only in the ASN field or the `autnum` field (in the routing templates) of Whois/RDAP, choose **Search Filter** and select **ASN (Autonomous System Number or Autnum)**.
Searching for an Entity (POC, Org, or Customer)
An entity represents information in a registry about organizations, corporations, governments, non-profits, clubs, individual persons, and informal groups of people. Different RIRs, IRRs, and registrars have different entities in their databases. For example, an entity in a registrar’s database could be the registrant of a domain (such as Google). In APNIC’s database, entities can include person, role, and Incident Response Team (IRT) objects. In ARIN’s database, entities include Points of Contact (POCs), Organizations, and Customers). Entities are given “handles,” or specific alphanumeric IDs, in ARIN’s database. Handles typically have the following formats:
- Org Handle, or Org ID: all capital letters (for example,
IANA); may contain a dash and suffix (for example,AKAMA-36) - POC Handle: all capital letters with a
-ARINsuffix (for example,KOSTE-ARIN) - Customer Handle: all capital letters with a
COprefix (for example,C00975227)
To search for an entity, enter its Handle into the search field and choose Search (for example, KOSTE-ARIN.)
The search filter defaults to “automatic” and returns results based on the type of search that the search function guesses you were trying to perform. In this example, the search engine auto-detects that you are searching for a POC handle and returns information about the POC. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with a POC search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
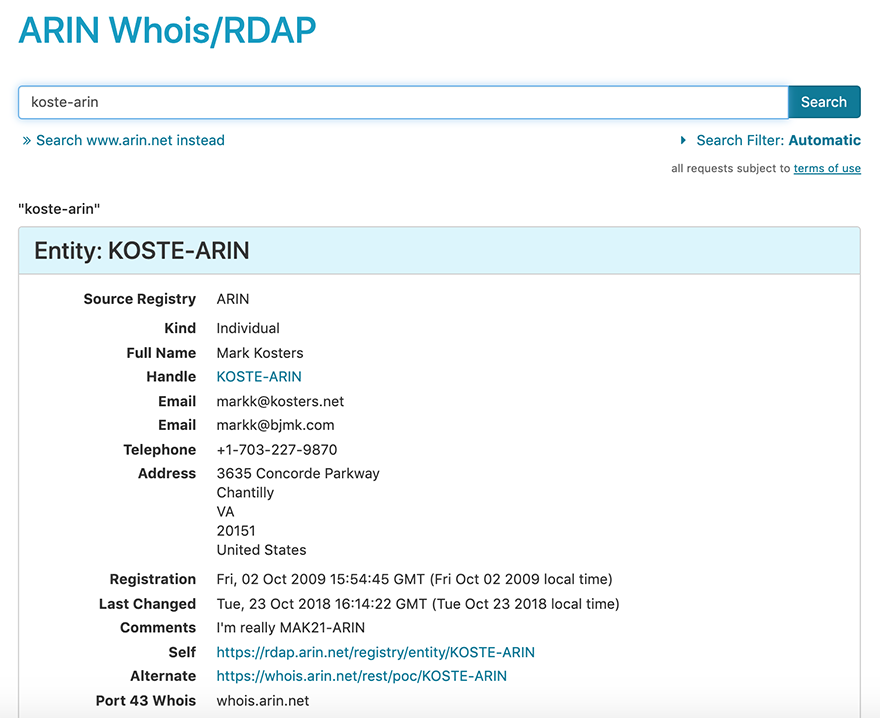
Choosing the Entity search filter searches Whois for only the entity that matches the search term you entered. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with an entity search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.

Searching with the “Entities by Full Name” Filter
You can perform a Whois/RDAP search in the Full Name field for the entity for which you are searching. If you are not sure of the exact full name, you can use wildcards (asterisks *) to substitute for missing information. For example, if you want to search for an organization that you know informally as “Yahoo,” searching on Yahoo* would return results with full names of Yahoo, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Inc., Yahoo! Broadcast Services, Inc., etc.
Searching for a Domain
You can search for either forward domain name or reverse domain information using Whois/RDAP. Forward domain names are used when translating IP addresses into hostnames (e.g., when you use example.com to reach an IP address such as 93.184.216.34). Since ARIN’s registry does not contain forward domain information, if you are searching for forward domains, your query will return results from a domain registrar (for example, Verisign), and the source of the results will be indicated in the footer or elsewhere in the results. Some registrars will not provide information for all fields in the result; for example, if the registrar does not collect that particular data, or if privacy laws prevent the registrar from sharing that data.
Reverse domain information (also called an “inverse address domain”) includes the “in-addr.arpa” or “ip6.arpa” domain name that is used in reverse DNS. Reverse domain information, along with pointer (PTR) records, is used to find the domain name associated with an IP address. If you are searching for the reverse domain associated with an IP address (for example, 2.0.192.in-addr.arpa that is associated with 192.0.2.0), the information will come from ARIN or the RIR where the reverse DNS is configured.
You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with a domain search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
Forward Domain
To find information for a forward domain name, the best practice is to enter it into the search field and choose the Domain filter. (The system may automatically detect some queries, but may miss others if Domain is not selected.) For example, to search for the example.com domain, enter example.com into the search field. Under Search Filter, choose Domain, as shown in the following example:
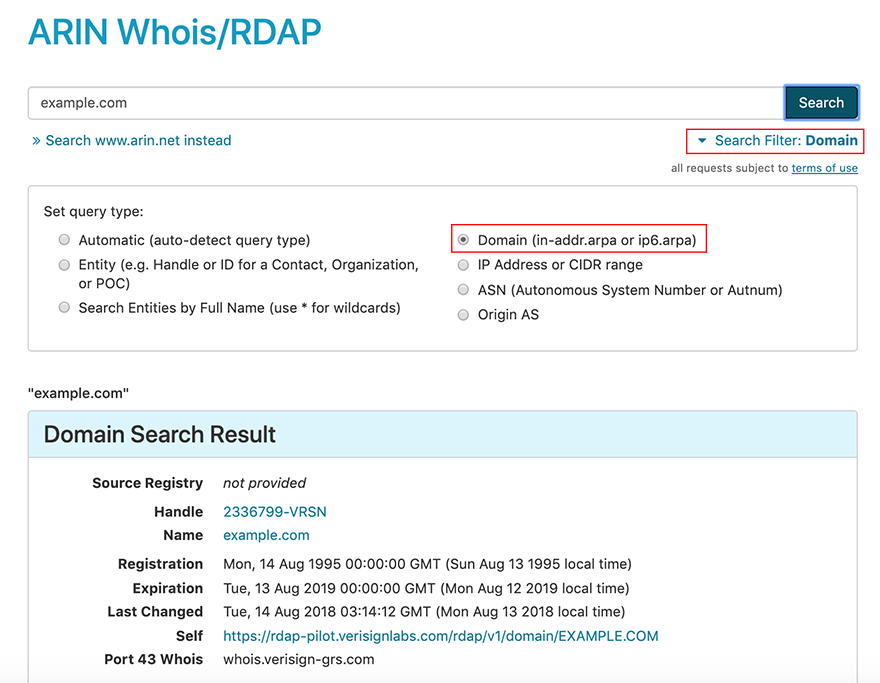
Reverse Domain
If you are searching for the domain associated with an IP address, enter the IP address in IPv4 (in-addr.arpa) or IPv6 (ip6.arpa) reverse domain format. For example, to get information about the zone serving the network 192.149.252.0, enter 252.149.192.in-addr.arpa in the search field and choose the Domain filter:
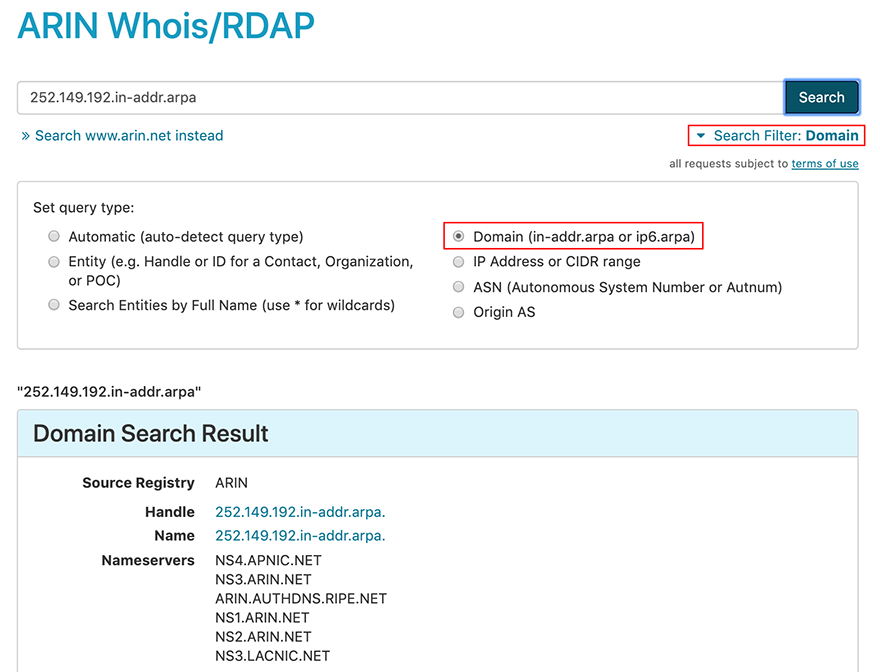
Searching for an Origin AS
To search for information in the Origin AS field of a record, enter the ASN in the search field and choose Origin AS as the search filter. Choosing this option performs a Whois/RDAP search for the Origin Autonomous System (AS) matching the search term you entered. Do not include the AS prefix. For example, to search for AS10745 in the Origin AS field, use 10745. You cannot use wildcards (asterisks *) with an Origin AS search in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
To prevent performance issues, an Origin AS query limits the returned networks to 256 results.
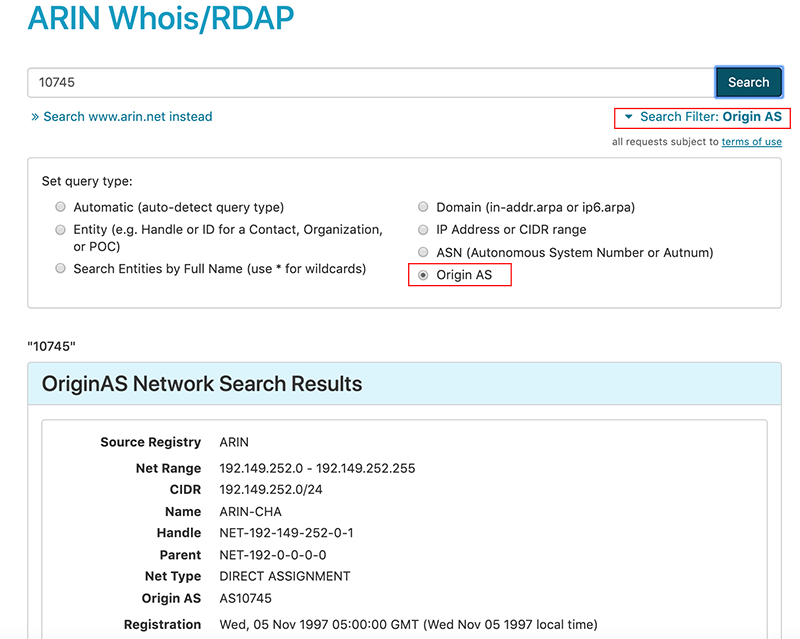
Tips and Helpful Information for Searching in Whois/RDAP
- Search terms are not case-sensitive.
- You can use wildcards (asterisks *) to search on partial information for full name searches. Substitute an asterisk (
*)for the missing part of the information you enter. You can use one or more wildcards at the beginning, middle, or end of your search term. Wildcards can only be used in automatic searches if the system determines you are searching for a full name. For example, the system will not search entities, in-addr.arpa or ip6.arpa domains, IP addresses, CIDR ranges, ASNs, or Origin AS fields using wildcards in ARIN Whois/RDAP.
Other Ways to Access Whois Data
- Whois-RWS: As of March 2019, ARIN’s featured Whois search service is Whois/RDAP. However, the older Whois-RWS is still available. Visit whois.arin.net and enter your search term in the search field. Visit Whois-RWS for more information.
- Whois Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): ARIN provides an API for both Whois/RDAP and Whois-RWS.
- Command-line interface: ARIN supports searching Whois using a CLI. Visit Searching Whois Using a CLI.
Interpreting Whois Results
Results for Whois/RDAP queries performed using the ARIN website or the command-line interface contain information about IPv4 and IPv6 address space, ASNs, POCs, and Orgs.
The type of results returned are indicated in the menu above each section. Results can include the following types:
Network
Network records (NETs) define a range of IPv4 or IPv6 addresses and show the organizations and POCs with authority over them.
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the network and provided it in response to the query. |
| Net Range | The IP address range of a network resource. |
| CIDR | The IP address block specified in CIDR notation. |
| Name | Name given to the network by the organization. |
| Handle | A unique auto-generated handle that identifies the network in the organization’s database. |
| Parent | The Handle of the parent IP address range. |
| Net Type | The type of network. For ARIN resources, these are: Direct Allocation (ISP), Direct Assignment (End user), Reallocated (downstream ISP customer), and Reassigned (end user customer). |
| Origin AS | Optional field collected during all IPv4 and IPv6 block transactions that records a list of the Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs), separated by commas or whitespace, from which the addresses in the address block(s) may originate. |
| Registration | Date of the initial registration of the resource. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the network object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the network object you retrieved. The alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the network object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema (using ARIN’s Whois-RWS server). This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the network object can be found. |
| Related Entities | Displays any entities, such as Orgs, POCs, or customers, that are associated with this resource. |
Origin AS Network
The Origin AS field is an optional field collected by ARIN during all IPv4 and IPv6 block transactions (allocation and assignment requests, reallocation and reassignment actions, transfer and experimental requests). This additional field is used by IP address block holders (including legacy address holders) to record a list of the ASNs from which the addresses in the address block(s) may originate. The Origin AS Network result shows information for the network that contains the Origin AS that you entered in the search field.
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the network and provided it in response to the query. |
| Net Range | The IP address range of the network associated with this Origin AS. |
| CIDR | The IP address block specified in CIDR notation of the network associated with this Origin AS. |
| Name | Name given to the network associated with this Origin AS by the organization. |
| Handle | A unique auto-generated handle that identifies the network associated with this Origin AS in the organization’s database. |
| Parent | The Handle of the parent IP address range for the network associated with this Origin AS. |
| Net Type | The type of network associated with this Origin AS. For ARIN resources, these are: Direct Allocation (ISP), Direct Assignment (End user), Reallocated (downstream ISP customer), and Reassigned (end user customer). |
| Origin AS | The Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) from which the addresses in the address block(s) may originate. |
| Registration | Date of the initial registration of the resource. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the network object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the network object you retrieved. The alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the network object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema (using ARIN’s Whois-RWS server). This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the network object can be found. |
| Related Entities | Displays any entities, such as Orgs, POCs, or customers, that are associated with this resource. |
ASN
ASN records, much like NET records, display the specific ASN and the Org with authority over it.
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the ASN and provided it in response to the query. |
| Number | Displays the number that represents an autonomous system (networks or connected groups of networks that adhere to a single unique routing policy that differs from the routing policies of their border peers). |
| Name | Name given to the ASN by the organization. |
| Handle | For ARIN data, number used to identify the AS in the database. Typically consists of the prefix AS and the AS number (for example, AS26299). |
| Registration | Date of the initial registration of the resource. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the ASN object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the ASN object you retrieved. The alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the ASN object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema (using ARIN’s Whois-RWS server). This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the ASN object can be found. |
| Related Entities | Displays any entities, such as Orgs, POCs, or customers, that are associated with this resource. |
Entity: Organization
Organizations are entities in RDAP, and the header of the search results will indicate “entity.” Organization information includes the Org ID to which resources are issued and the contact information for the Org. Customers to whom resources are reassigned are also displayed in as an entity, with the customer handle in the menu.
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the network associated with this organization and provided it in response to the query. |
| Kind | The type of entity (for Organizations in ARIN’s database, this will be “Org;” results from other RIRs may use different terminology). |
| Full Name | The name of the Organization who is assigned the resource(s). |
| Handle | A unique alphanumeric ID that identifies the organization in the RIR or registrar’s database. |
| Address | Typically the location information for a resource, an organization, or POC. May not always reflect the exact physical location of the actual resource, org, or POC, as there is no policy requirement to do so. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Data Policy | ARIN adds this information to denote that the response is truncated, or that data or results are limited and some have been were omitted. This is done, for example, in cases where displaying many results would negatively impact the performance of the Whois query. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the entity object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the entity object you retrieved. Because ARIN operates its Whois-RWS server, the alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the entity object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema. This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the entity object can be found. |
| Related Entities | Displays any entities, such as Orgs, POCs, or customers, that are associated with this resource. |
| Related Networks | Displays networks that are associated with this Org. |
| Related Autnums | Displays ASNs that are associated with this Org. |
Entity: POC
POCs are entities in RDAP, and the header of the search results will indicate “entity.” POC information can include a name, mailing address, and contact information. POCs can be an individual (person) or a group. ARIN data includes different types of POCs (Administrative, Technical, Abuse, Network Operations Center [NOC], Routing, and DNS), and the type is noted in the “Roles” field.
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the network associated with this entity and provided it in response to the query. |
| Kind | The type of the POC: individual or group. |
| Full Name | The full name of the POC. |
| Email addresses for the POC. | |
| Telephone | Telephone number of the POC. |
| Organization | For ARIN data, if the POC is a group POC, the name of the group is given here. |
| Address | Typically the location information for a resource, an organization, or POC. May not always reflect the exact physical location of the actual resource, org, or POC, as there is no policy requirement to do so. |
| Roles | For ARIN data, this indicates the type of POC: Administrative, Technical, Abuse, NOC, Routing, or DNS POC. |
| Registration | Date of the initial registration of the resource. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Comments | Text comment that applies to the POC. There can be multiple Comment fields displayed in a result. These comments are typically added by an organization POC. |
| Data Policy | ARIN adds this information to denote that the response is truncated, or that data or results are limited and some have been were omitted. This is done, for example, in cases where displaying many results would negatively impact the performance of the Whois query. |
| Unvalidated POC | For ARIN data, this message indicates that ARIN has attempted to validate the POC, but has received no response from the POC since the listed date. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the entity object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the entity object you retrieved. Because ARIN operates its Whois-RWS server, the alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the entity object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema. This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the entity object can be found. |
Domain
Domain results include information about forward domain names (for example, google.com), reverse domain information (for example, the “in-addr.arpa” or “ip6.arpa” domain names), and nameservers (for example, NS1.ARIN.NET, NS2.ARIN.NET).
| Result Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Registry | The name of the RIR, IRR, registrar, or other entity that maintains the registration information for the domain or the reverse domain and provided it in response to the query. |
| Handle | The name of the forward domain or reverse domain delegation. For ARIN data, the Handle and Name field are the same. |
| Name | The name of the forward domain or reverse domain delegation. For ARIN data, the Handle and Name field are the same. |
| Nameservers | The name of one or more nameservers for a domain object. There can be multiple nameservers shown. |
| Registration | Date of the initial registration of the resource. |
| Expiration | Date that the registration of the resource expires. |
| Last Changed | Date when the registration information for the resource was last updated. |
| Self | The link representing the URL (address) of the object you retrieved; this field is used for client-side caching. |
| Alternate | An alternate representation of the object you retrieved. Because ARIN operates its Whois-RWS server, the alternate field for ARIN results will be populated with a link to the data for the entity object in XML format, with an ARIN-specific schema. This field may not be populated for other RIRs and registrars. |
| Port 43 Whois | A simple string containing the fully-qualified host name or IP address of the WHOIS [RFC3912] server where the object can be found. |
Getting Help with Whois
- For operational problems with Whois, please log in to your ARIN Online account and create an Ask ARIN ticket, or contact the ARIN Help Desk with the appropriate details.
- To report inaccurate information in Whois, you can file a report online.

